Six Thinking Hats (6TH)
The Thinking Hats is a role-play method, in which different perspectives are represented by six hats of different colors. When a participant is symbolically wearing a specific hat, they must seek to perceive the situation through the lens associated with that color. This method allows parallel thinking and shows how different aspects of one's personality can approach a problem differently.
Organisation
-
Duration
Medium (about 30-60 minutes)
-
Complexity
Simple
-
Group size
2 to 30 persons
This activity is suitable online.
Description Long
The Six Thinking Hats method was first introduced by Dr. Edward de Bono in the early 1980s as a parallel thinking process with the aim of making its users more productive, focused, and mindfully involved as a group. The key point is that each hat represents a direction to think rather than a label for thinking. This tool assists in the critical analysis of complex situations by simulating diverse points of view in a controlled environment. Additionally, this technique helps to achieve more comprehensive perspectives and sounder solutions, by forcing the participants to step outside the limits of their standard thought processes and points of view.
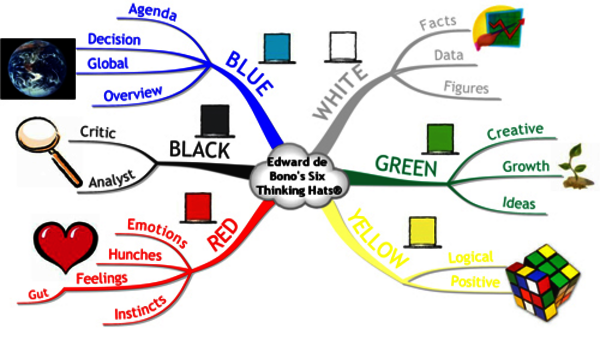
In this method, thinking is divided into six solid roles and functions distinguishable by a specific color of symbolic "thinking hat." The six color hats and the key words they represent are given below:
White Hat (white paper) - focuses on available information and data (known facts and figures) from a neutral and objective point of view.
Red Hat (fire and warmth) - represents emotions, hunches, intuition and feelings; its focus is on prompt expression without explanation nor justification.
Black Hat (stern judge wearing black robe)- being judgmental and critical of how/where something could possibly go wrong (identify the cons of the suggestion);
Yellow Hat (sunshine)- explores optimism, benefits and brightness (exploration of the positives);
Green Hat (vegetation) - creativity and lateral thinking; its emphasize is on change, innovation, invention; new ideas, possibilities, concepts, perceptions, paradigms.
Blue Hat (sky, cool) - management and control of thinking process (making certain that Six Thinking Hats rules are adhered to).
Illustration
Preparation
- Arrange the room to allow for conversation in small groups according to the number of participants.
- Write down and describe the characteristics/opinions of each colored hat in detail and post clearly visible reminders in the working space.
Online: make sure that there are enough online sub-meetingrooms that groups can enter and leave.
Execution
- Choose a moderator to introduce the problem and present background information on the subject matter to the attendees.
- Instruct participants to break into groups and ask each group to select a color hat to begin with. An alternative approach is for the groups to all start out wearing the same hat and then move on to the other ones, in an order predetermined by the facilitator.
- Assign facilitators for each group, or ask participants to select their own facilitator. The role of facilitator is to guide a productive discussion.
- Move between groups to ensure that participants remain disciplined in their assigned perspectives and that the conversations are progressing according to the learning objectives.
- Following all their explorations under each colored hat, instruct the groups to collaboratively evaluate the outcomes of their process and establish action items to solidify the lessons learned.
- Each small group must identify a reporter to provide a summary of conclusions to the larger group.
- Summarize the results and communicate them for future reference if appropriate.
Hints from experience
If hats are not available or culturally appropriate, use T-shirts, colored cards or badges, or colored pens instead.
Establish collaborative group dynamics before the exercise, either through suitable ice-breakers or by scheduling the session in the middle of a course. As with most role-play exercises, this one works best if the participants are confident.
The facilitator should initially explain to the participants that they are going to view the problem in six different ways. Each hat represents a way of thinking. There will be 6 types of thinkers�when they are in that role will only address the issue from that particular perspective.
If participants seem to be facing barriers or losing control of the process, they may make an emergency switch of roles to the hat that will best help them deal with the challenges being faced. For instance, the "creative" green hat can help find new ideas and the "managerial" blue hat can be used to reduce chaos.
Tools list
- Hats, colored
- Flipchart or Whiteboard
- Copies of role descriptions (six hats)
- Writing utensils, pen, pencil
References
Creatingminds.org,. Six Thinking Hats. Retrieved 28 October 2015, from http://creatingminds.org/tools/six_hats.htm
De Bono Six Thinking Hats Mind Map. Retrieved from https://www.illumine.co.uk/resources/thinking-learning/how-to-think/de-bono-six-thinking-hats-mind-map/
De Bono, E. (1985). Six thinking hats: An Essential Approach to Business Management. Boston: Little, Browne and company.
De Bono, E. (1999). Six thinking hats. Boston: Back Bay Books.
Entrepreneurial Insights,. (2015). Brainstorming - Techniques for Idea Generation. Retrieved 29 October 2015, from http://www.entrepreneurial-insights.com/brainstorming-techniques-for-idea-generation/
Innosupport.net,. InnoSupport - Supporting Innovation in SME: 4.8 Six Thinking Hats. Retrieved 29 October 2015, from http://www.innosupport.net/index.php?id=2150&L=wsiilwuplqf
Kstoolkit.org,. Knowledge Sharing Tools and Methods Toolkit - DeBonos Six Thinking Hats. Retrieved 28 October 2015, from http://www.kstoolkit.org/DeBonos+Six+Thinking+Hats